
Procedural
Requirements
Effective Date: June 27, 2013
Expiration Date: December 31, 2027

|
NASA Procedural Requirements |
NPR 4300.1C Effective Date: June 27, 2013 Expiration Date: December 31, 2027 |
| | TOC | Preface | Chapter1 | Chapter2 | Chapter3 | Chapter4 | Chapter5 | Chapter6 | Chapter7 | Chapter8 | Chapter9 | Chapter10 | Chapter11 | Chapter12 | AppendixA | AppendixB | AppendixC | AppendixD | AppendixE | AppendixF | AppendixG | AppendixH | ALL | |
7.1.1 This chapter sets forth the authority and procedures for disposing of NASA-owned property located in foreign countries. Whenever NASA-owned property is to be located in a foreign country as part of a partnership or loan, the final disposition should be addressed in the initial international agreement. Figure 7-1 provides a flow chart of the various options available to NASA for disposal of excess property located overseas.
7.1.2 "Foreign excess property" is any United States-owned excess property physically located outside the United States, the U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, Palau, and the Northern Mariana Islands. (41 C.F.R. 102-36.40, Definitions).
7.2.1 The disposition of NASA-owned foreign property shall conform to the foreign policy of the United States (Foreign Excess Property, 40 U.S.C., Chapter 7) and the terms and conditions of any applicable international agreement, export/import laws, regulations, and U.S. security or trade export controls policy as determined in consultation with NASA Headquarters Office of International and Interagency Relations (OIIR).
7.2.1.1 Disposition options for disposal of foreign excess property are: utilization by NASA or another U.S. Federal agency; return to the United States; donation of medical materials or supplies to nonprofit medical or health organizations; sale, exchange, lease, or transfer of such property to the foreign country for cash, credit, or other property; or abandonment, destruction, or donation of such property when it has been determined by NASA that it has no commercial value or the estimated cost of care and handling would exceed the estimated proceeds from its sale.
7.2.1.2 The disposal of NASA foreign excess property shall be conducted with the coordination and approval of the United States Diplomatic Mission in the country concerned (41 C.F.R. 102-36.385(d)) in coordination with NASA Headquarters DPM and OIIR.
7.2.2 Each NASA Center, in consultation with the NASA Headquarters DPM, shall be responsible for dispositioning NASA-owned excess property physically located in a foreign country that is no longer needed to fulfill that Center's responsibilities.
7.2.3 All property dispositioned to any foreign governments or entities located in a foreign country shall include a condition forbidding its importation into the United States unless the Secretary of Agriculture (in the case of any agricultural commodity, food, or cotton or woolen goods) or Secretary of Commerce (in the case of any other property) have approved importation of the property.
7.2.4 All disposal of NASA-owned excess property located in a foreign country dispositioned to any foreign governments or entities shall be reported to the U.S. State Department in consultation with OIIR.
7.2.5 Proceeds (in U.S. funds or foreign currency reduced to U.S. funds) from sale of foreign property (other than exchange/sale) shall be deposited in the Treasury Department as Miscellaneous Receipts (40 U.S.C. § 705).
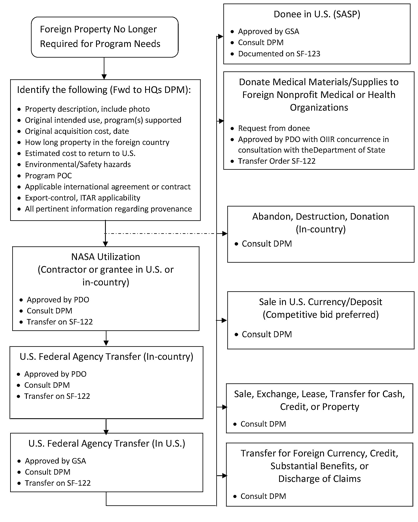
Figure 7-1. Process Flow Chart for Disposition of NASA Property
Located in Foreign Countries
7.2.5.1 Proceeds in foreign currency not reduced to U.S. funds shall be handled in accordance with Treasury Department procedures (40 U.S.C. § 705(c)).
7.3.1 The Director, LD, as delegated by the Assistant Administrator for OSI, is responsible for policies, procedures, and any other matters related to the disposal of NASA-owned foreign excess property, subject to provisions of applicable laws and regulations and issues the appropriate NASA policies and guidelines covering foreign disposal.
7.3.2 The Headquarters DPM shall consult the NASA Headquarters OIIR to determine whether there is an international agreement that establishes appropriate property disposition or export controls that may apply to existing disposition procedures.
7.3.3 The Center PDO is responsible for the disposition of NASA excess property located in a foreign country assigned or accountable to the respective NASA Center.
7.3.4 The Center PDO shall keep the Headquarters DPM informed of proposed foreign excess property disposal actions, problems, or other matters related to the disposal of foreign property.
7.3.5 Center PDOs shall identify all NASA-owned excess property located in a foreign country to be dispositioned and provide the property information to the Headquarters DPM as outlined in section 7.6.1.
7.3.6 The Center PDO shall coordinate with the CEA to determine ITAR/export control considerations for foreign excess disposition.
7.3.7 The Center PDO shall coordinate with the Center OCIO, and/or the CISO to determine sanitization considerations prior to disposition of digital media as defined in NPR 2810.1 and Chapter 3 of this NPR.
7.4.1 The disposal of NASA property that is currently in a non-U.S. (overseas) location, which has been identified as excess, may impact the foreign policy and national security of the United States, and may result in a transfer that impacts technology or trade issues between the United States and other countries' customs, import and export control laws and regulations.
7.4.2 Foreign property disposition requests and decisions shall be reviewed by the Headquarters DPM, Headquarters Export Administrator (HEA), and OIIR to ensure adherence to property disposition requirements, international agreements, and applicable export control requirements.
7.4.3 In some cases, NASA disposal policy may be found to be in conflict with existing Department of State or NASA country-to-country agreements. Copies of any agreements should be provided to the Headquarters DPM and OIIR for review of applicable deviations pertaining to the unique disposition of the property.
7.5.1 Whenever in the best interest of the Federal Government, disposal processing of excess foreign property under the control of a NASA Center in the United States may be conducted as normal Agency excess property.
7.5.1.1 The Center PDO shall document and concur with any decision to return foreign property to the United States for disposal processing.
7.5.1.2 The decision to return foreign property to the United States may be made after the property has been screened as described in sections 7.7 and 7.8, or it has been determined that the property should not be disposed of in the foreign country of location.
7.5.1.3 Consideration should be given to preventing new procurements of similar items, transportation cost, packing cost, and retention of title to the property in the Federal Government.
7.5.2 The first potential method of disposal may be NASA approved utilization by NASA organizations (including NASA contractors in a current contractual relationship when authorized by the respective CO) or NASA grantees located in the United States and its territories or a foreign country. For this type of disposal, the Center PDO will approve the appropriate transfer documents in consultation with the Headquarters DPM. No higher level of concurrence or approval is required.
7.5.2.1 Only NASA excess property may be furnished to a NASA grant recipient.
7.5.2.2 Assistance in deciding between similar requests for the same property may be referred to the Headquarters DPM.
7.5.3 The second potential method of disposal may be NASA approved transfer to another U.S. Federal agency (in a foreign country) for continued use or disposal processing.
7.5.3.1 Transfers for continued use by another U.S. Federal agency in a foreign country will not be approved until NASA has determined it has no reuse for the property in consultation with the Headquarters DPM.
7.5.3.2 The other U.S. Federal agency Ordering Official and the Center PDO shall approve the SF 122, Transfer Order. No higher level of concurrence or approval is required.
7.5.3.3 Assistance in deciding between similar requests may be referred to the Headquarters DPM.
7.5.4 The third potential method of disposal may be GSA-approved transfer of excess property to another U.S. Federal agency for use in the United States.
7.5.4.1 Transfers to another U. S. Federal agency and return to the United States for use will not be approved until NASA has determined it has no reuse for the property in consultation with the Headquarters DPM.
7.5.4.2 Property shall not be released by NASA holding activities until NASA has received the SF 122, Transfer Order, bearing the signed approval of the appropriate GSA official. No higher level of concurrence or approval is required.
7.5.4.3 Direct costs for the return of foreign property to the United States under the provisions of 40 U.S.C. § 702(b) require that transportation costs for returning foreign excess property to the United States are paid by the U.S. Federal agency receiving the property.
7.5.5 The fourth potential method of disposal may be GSA-approved transfer of surplus property to an eligible donee and return to the United States for use.
7.5.5.1 In accordance with 41 C.F.R. 102-37, transfers to an eligible donee (via the SASP) for return to the United States for use should not be approved until NASA has determined it has no reuse for the property and no other U.S. Federal agency has shown an interest in acquiring the property in consultation with the Headquarters DPM.
7.5.5.2 Property shall not be released by NASA-holding activities for donation until NASA has received the SF 123, Transfer Order Surplus Property, bearing the signed approval of the appropriate GSA official. No further levels of concurrence or approval are required.
7.5.5.3 The State agency representative shall arrange for the shipment of property approved for donation and allocated by GSA to State agencies for distribution to an eligible donee. 40 U.S.C. § 702(b) requires that transportation costs and direct costs incurred incident to donation, including packing, handling, and crating for returning foreign excess property to the United States are paid by the State agency or donee receiving the property.
7.5.6 A fifth disposition method may be donation of medical materials to foreign nonprofit health organizations. In accordance with Foreign Excess Property, 40 U.S.C., Chapter 7, section 703(b) and (c), NASA may approve the donation of medical materials or medical supplies for use in any foreign country only to nonprofit medical or health organizations, including those qualified to receive assistance under sections 214(b) or 607 of the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961 (22 U.S.C. § 2174(b), pt. 2357).
7.5.6.1 The advice of the OIIR shall be obtained as to how donation of medical materials or medical supplies to foreign nonprofits will best serve the U.S. foreign policy interests and objectives in the area.
7.5.6.2 The advice of OIIR shall be given consideration in reaching a decision as to the recipient of the medical materials or medical supplies to be donated.
7.5.6.3 Assistance in verifying information on the activities or organizations unknown or not familiar to the NASA Center should be requested from OIIR.
7.5.6.4 The local American Red Cross should be advised and offered property that can be readily identified as originally processed, produced, or donated by the American Red Cross before donating to other agencies (41 C.F.R. 102-37.540 - 555).
7.5.6.5 A request from the potential donee for the medical materials and medical supplies shall be made in writing and contain, as a minimum:
a. A brief statement describing the activities of the organization or institution.
b. General information on the planned use of the requested property or the need and purpose of the property.
c. A statement that the property will not be resold or put to use for any other purpose.
7.5.6.6 In addition to the donee's request for foreign property, the Center PDO shall complete and forward an SF 122 to the Headquarters DPM for OIIR review and concurrence in consultation with the Department of State pending transfer.
a. The Center PDO shall include a requirement for compliance with U.S. Department of Commerce and Department of Agriculture regulations when transporting any personal property back to the United States.
7.5.6.7 Donations shall be effected without cost to NASA.
7.5.7 The sixth potential method of disposal may be sale with proceeds in U.S. currency or reduced to U.S. currency deposited into the U.S. Treasury as miscellaneous receipts.
7.5.7.1 As determined by NASA, other U.S. Federal agency screening, and donation screening, any remaining NASA-owned foreign property may be sold by competitive bid processes whenever feasible. The sale of NASA-owned foreign property will be conducted by:
a. Foreign Service post, U.S. Department of State;
b. GSA;
c. U.S. military installation;
d. Approved agency of a foreign government; or
e. NASA, including NASA cost reimbursement contractors or grantees (41 C.F.R. 102-38, Sale of Property).
7.5.7.2 Whenever NASA-owned property is located in a foreign country, the Center PDO should establish plans for the potential future sale of the property.
7.5.7.3 The preferred sales method is to use the services and facilities of U.S. Foreign Service posts, U.S. military installations, or GSA to sell NASA-owned foreign property whenever approved arrangements can be effected. The Headquarters DPM should be consulted.
7.5.7.4 Sales of NASA-owned foreign property by a U.S. Foreign Service post or U.S. military installation will be processed according to the directives and procedures of that installation.
7.5.7.5 The services and facilities of any agency of a foreign government in which the foreign property is located shall be used when an approved International Agreement or Treaty exists between the U.S. Government and the respective foreign government to ensure:
a. Compliance with U.S. foreign policy.
b. Identification of any limitations on the transfer of technology and certain types of property to specific countries.
7.5.7.6 Copies of any such agreements or treaties shall be provided to the Headquarters DPM and OIIR.
7.5.7.7 Sale proposals of NASA-owned foreign property by any agency of a foreign government in the country in which the foreign property is located shall be forwarded to the Headquarters DPM for OIIR review and concurrence in consultation with the NASA OGC and the U.S. Department of State.
a. Sales proposals shall include:
(1) A copy of the approved finding for proposed sale;
(2) A statement as to necessity for NASA to effect the sale;
(3) The designation and address of the proposed seller;
(4) The name of activity and location of property to be sold;
(5) A complete commercial description of the property to be sold including manufacturer, manufacture date, quantity, condition, acquisition cost, features, capabilities, and country of origin; and
(6) The intended end use of the property to be sold.
(7) A requirement for compliance with U.S. Department of Commerce and U.S. Department of Agriculture regulations when transporting any personal property back to the United States.
7.5.8 The seventh potential method of disposal may be NASA-approved abandonment, destruction, or donation of foreign property that has no commercial value or for which the estimated cost of care and handling would exceed the estimated proceeds from sale.
7.5.8.1 Abandonment and/or destruction (A&D) shall not take place unless it can be demonstrated in writing that the property has no commercial value or if estimated costs of care and handling exceed the estimated proceeds from sale.
7.5.8.2 Property in the host nation that cannot be offered for sale (restricted items) because of U.S. national interests or is dangerous to public health and safety shall not be abandoned or destroyed without concurrence from OIIR in consultation with the U.S. Department of State.
7.5.8.3 The proposed A&D process and details shall be documented by the Center PDO using NF 812, Determination and Authorization to Abandon or Destroy Surplus Property.
7.5.8.4 The Center PDO shall forward the NF 812, Determination and Authorization to Abandon or Destroy Surplus Property to the Headquarters DPM pending review and occurrence.
7.5.8.5 With the exception of NASA-owned property restricted by U.S. foreign policy, including technology transfer or property dangerous to public health and safety, NASA-owned property may be donated instead of taking A&D actions, without cost to the U.S. Government, to:
a. Any organization, institution or agency of any friendly foreign government or local subdivision thereof; and
b. Any nonprofit scientific, literary, educational, public health, public welfare, or charitable institution or any hospital or similar institution, organization, or association in a friendly country, provided its activities are not adverse to the interests of the United States.
7.5.8.6 In addition to the donee's request for foreign property, the Center PDO shall complete and forward an SF 122 to the Headquarters DPM for OIIR review and concurrence in consultation with the U.S. Department of State.
a. The Center PDO shall include a requirement for compliance with U.S. Department of Commerce and U.S. Department of Agriculture regulations when transporting any personal property back to the United States.
7.5.9 The eighth potential disposition method may be disposal by exchange, lease, or transfer for cash, credit, or other property consideration with or without warranty and upon such terms and conditions as the Center PDO deems appropriate. Any such proposal shall be documented by the Center PDO and forwarded to the Headquarters DPM for OIIR for review and concurrence in consultation with the NASA OGC and the U.S. Department of State.
7.5.9.1 The proposal shall include:
a. Method of disposition;
b. Applicable warranties;
c. Method of reimbursement;
d. Detailed description of the property as provided in paragraph 7.6.1; and
e. All applicable terms and conditions for the transaction.
7.5.10 The final potential disposal method may be any disposal for foreign currencies or credits, substantial benefits, or the discharge of claims resulting from the compromise or settlement of such claims by NASA in accordance with the law, whichever OIIR finds to be most practical and advantageous to the Government. Any such proposal shall be documented by the Center PDO and forwarded to the Headquarters DPM for OIIR review and concurrence in consultation with the NASA OGC and the U.S. Department of State.
7.5.10.1 The proposal shall include the same information provided in paragraph 7.5.9.1 as well as the rationale for choosing this disposition method.
7.6.1 Prior to reporting foreign property for disposal processing, the Center PDO shall prepare a disposition proposal (disposal case) and, in coordination with the disposing organization, provide the following information to the Headquarters DPM:
a. Description of property including photo (if obtainable).
b. The original intended use for the property and program(s) it supported; whether the memorandum of understanding, loan, or project agreement has ended; and, if so, when.
c. Original acquisition cost.
d. How long the property has been in the foreign country, provenance.
e. Original purchase date.
f. Estimated cost for returning the property to the United States (e.g., transport, scrap, sale) if available.
g. Estimated cost for disposition of the property in the United States (e.g., transport, scrap, sale) if available.
h. All environmental and safety hazards associated with the property.
i. Point of contact (POC) from the program with knowledge of the property and its use (name, e mail address, phone number).
j. Knowledge of any international agreement associated with the property (specifically or generally) with a copy of the agreement if available.
k. Export-control considerations associated with the property or any part of the property, including the category of controls and specifics on any pieces that are export controlled.
l. Interest (foreign or domestic) in the disposition of the property (e.g., return, transfer, sale, exchange, abandonment, destruction, donation).
m. Any cost (e.g., storage cost) incurred if the item is not transferred.
n. Whether equipment is under the control of a contractor.
o. Benefit justification if items are recommended to be retained in the foreign country.
7.6.2 Excess NASA-owned property located in foreign countries may be reported for disposal processing in the same manner domestic property in GSAXcess®.
7.6.3 In order to determine proper disposition of the property, complete commercial descriptions, including features and capabilities are required. Depending on the final disposition of the property, it may be necessary to identify if an export license was involved for property shipped from the United States. Also, property manufactured or purchased in a foreign country should be identified by the Center PDO in the disposition proposal since there may be import restrictions to the United States.
7.6.4 The Export Administration Act of 1979, the Department of Commerce (15 C.F.R., Chapter VII, 770-779) may require more descriptive information and may determine if the property may be disposed of in the foreign country.
7.7.1 NASA-owned property may undergo internal NASA-wide screening as follows:
7.7.1.1 NASA internal agency screening may take place for 0 to 21 calendar days using DSPL.
7.7.1.2 The Center PDO should consult the Headquarters DPM to determine how potential NASA artifacts may be dispositioned.
7.7.1.3 Center PDOs may review PCARSS or manual lists, as available, to determine the availability of contractor inventory when requests for property are received from programs or procurement activities.
7.8.1 Other U. S. Federal agencies located in foreign countries may screen NASA foreign property concurrently with Federal agencies within the United States using GSAXcess® or through other methods if NASA foreign excess property is made available for external screening. Donation screening will be performed concurrently; however, property may only be donated by GSA if it becomes surplus to the Federal Government.
7.9.1 The Center PDO shall prepare a written disposal case in DSPL on all foreign excess property. A disposal case number will not be closed until the final disposition has taken place.
7.9.2 Centers disposing of foreign excess property shall maintain complete records of all disposals in accordance with NPR 1441.1.
| TOC | Preface | Chapter1 | Chapter2 | Chapter3 | Chapter4 | Chapter5 | Chapter6 | Chapter7 | Chapter8 | Chapter9 | Chapter10 | Chapter11 | Chapter12 | AppendixA | AppendixB | AppendixC | AppendixD | AppendixE | AppendixF | AppendixG | AppendixH | ALL | |
| | NODIS Library | Property, Supply and Equipment(4000s) | Search | |
This document does not bind the public, except as authorized by law or as incorporated into a contract. This document is uncontrolled when printed. Check the NASA Online Directives Information System (NODIS) Library to verify that this is the correct version before use: https://nodis3.gsfc.nasa.gov.